Recognizing that most environmental issues are best addressed through international cooperation, today there are a myriad of international policy processes meant to address the pressing challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss and sustainable development. The world of international policy – one of conference centres and country name plates; far away from mangrove forests – plays a key role in increasing global action to conserve and protect coastal blue carbon ecosystems. Within these international policy processes, such as the United Nations conventions on climate change and biodiversity, countries come together to set ambitious goals, take on-the-ground action at the national level, and share what they have achieved to date.
However, many of these policy processes were established decades ago, in isolation from each other, often making it difficult for countries to collaborate across their closely-related themes of climate change, biodiversity and sustainable development.
To help address this challenge, Conservation International and IUCN, along with partners, are working to accelerate the conservation and restoration of blue carbon ecosystems globally by increasing synergies across these often siloed, disconnected conversations. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the 2030 Agenda and related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) are the key policy processes relevant to conserving and restoring blue carbon ecosystems. Shifting from traditionally siloed approaches to integrated approaches across these policy processes holds the potential to deliver high-quality outcomes for coastal blue carbon ecosystems, which will allow countries to:
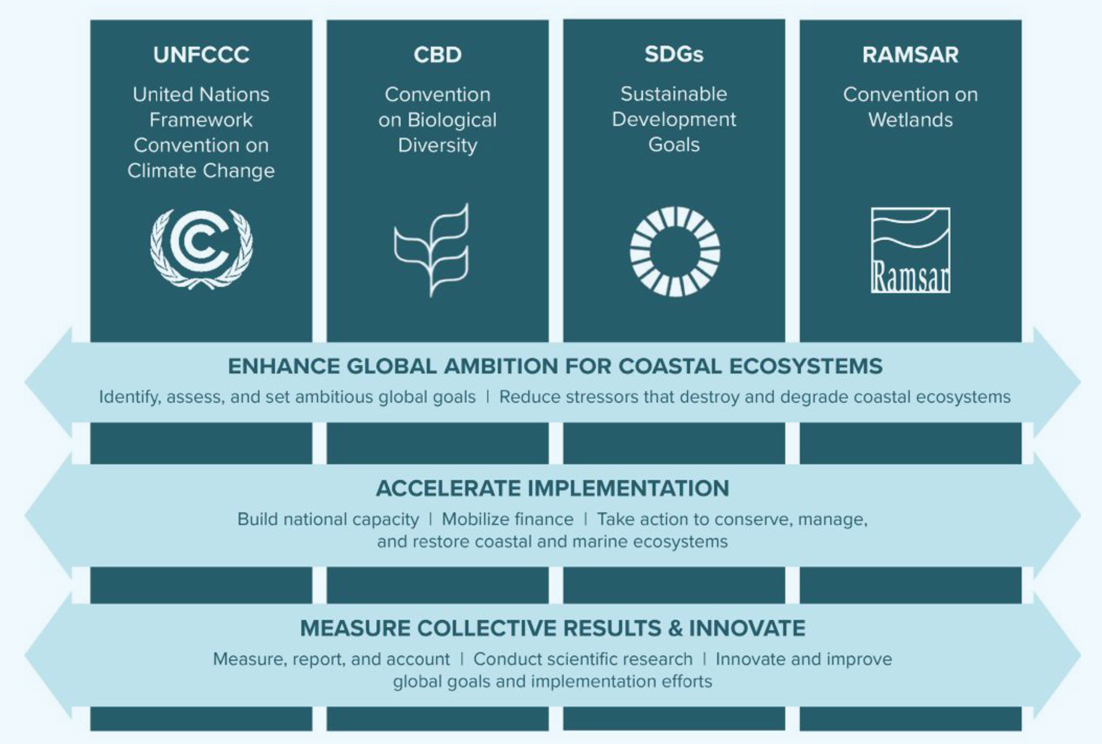
Some of the key reasons to support increased synergy and collaboration across policy processes, and steps countries can take to achieve these goals:
1. Aligning goals for blue carbon ecosystems can increase global ambition, leading to more - and better - outcomes on the ground.
2. On-the-ground conservation and restoration can be implemented more efficiently and effectively.
3. Supporting synergies can promote innovation and better measurement of conservation and restoration outcomes.
Further details on how the conservation and restoration of coastal blue carbon ecosystems can be accelerated and enhanced through aligned international policies, including recommendations for countries to take action, can be found in Conservation International and IUCN’s Blue Carbon Policy Framework.
Authors: Dorothée Herr, Manager Oceans and Climate Change, IUCN; Victoria Romero, Policy Officer, Biodiversity, IUCN; Jill Hamilton, Director, Blue Climate Strategy, Conservation International (CI); and Elizabeth Francis, International Blue Carbon Policy Consultant.
Originally published by ECO ECO22 SI2 Coastal Blue Carbon (ecomagazine.com)
